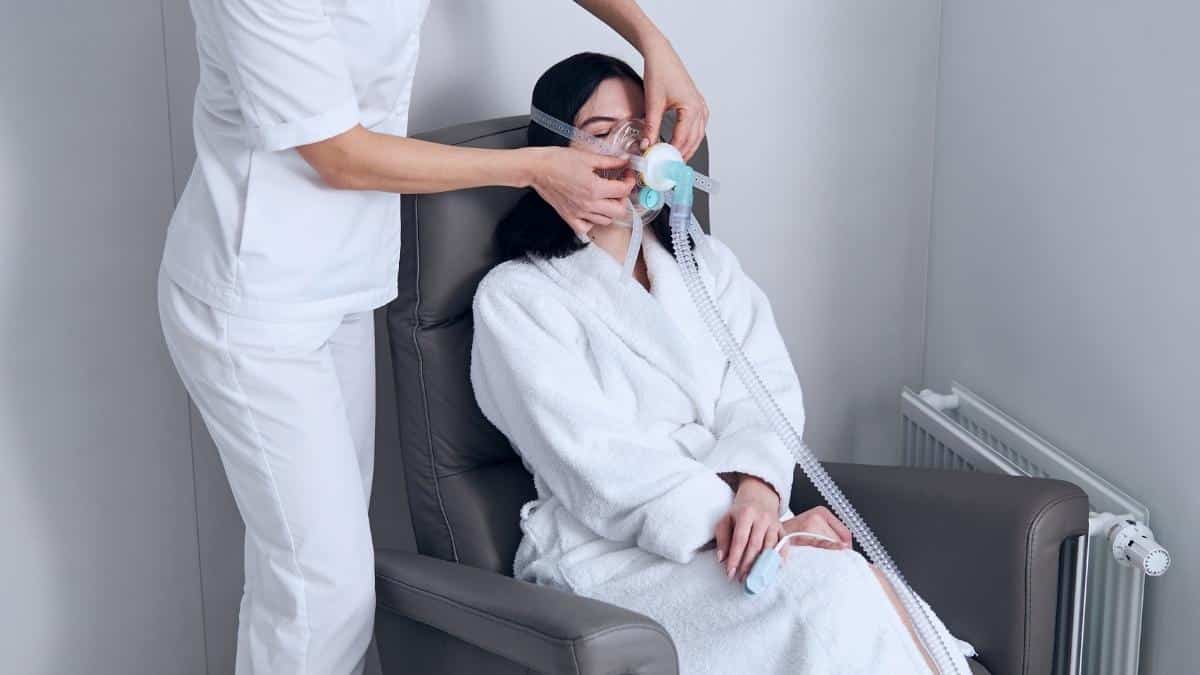
Doctors often prescribe oxygen therapy at home for people with chronic lung disease and low blood oxygen levels. Doctors and COPD patients keep a close eye on blood oxygen levels.
Oxygen is essential to a properly functioning body. Every cell, organ and tissue in your body needs enough oxygen. Healthy oxygen levels help keep your body working at its best.
However, for people with COPD and other chronic lung diseases, maintaining a healthy blood oxygen level can be difficult. Chronic lung diseases make it hard for people to breathe normally and get enough oxygen from the air.
When you use oxygen therapy, it helps you maintain a healthier blood oxygen level. While oxygen therapy at home is safe, it’s still important to follow safety guidelines.
Check out these basic safety tips for oxygen therapy at home.
5 Oxygen Therapy At Home Safety Tips
If your doctor has prescribed oxygen therapy at home, then it’s important to follow simple safety tips. These safety tips can be used regardless of the type of oxygen equipment you have.
While oxygen itself is not flammable or combustible, oxygen may act as an accelerant and make everything in an oxygen-rich environment burn faster and hotter.
Following safety guidelines helps you ensure that you safely receive the most out of your oxygen therapy at home.
1. Avoid Open Flames
Since oxygen can cause things to burn faster and hotter, avoiding open flames may seem obvious. However, open flames are more common than you might think.
For example, burning a candle in your home is considered an open flame. In general, it’s advised to stay at least 5-10 feet away from gas stoves, lighted fireplaces, woodstoves, candles and other sources of open flames.
In addition, keep at least 6 feet away from any source of fire while dining at restaurants.
2. Use Caution in the Kitchen
Everyone must cook sometimes. So, using caution as you cook remains especially important for people using oxygen therapy at home. Don’t wear loose fitting clothing or long sleeves while cooking.
Also, keep oxygen equipment away from any sources of heat, including the stove top and oven. Certain cooking materials, such as oil and grease, are highly flammable. Avoid splattering grease and oil because it can catch fire easily and burn quickly in the presence of oxygen.
Microwaves are one of the safest kitchen appliances you can use while on oxygen. In general, keep oxygen 6 feet away from sources of heat.
3. Stay Away from Electrical Equipment
Besides direct heat, sparks from electrical equipment can be hazardous around oxygen therapy at home. Avoid using electric razors and electric toothbrushes while using oxygen.
Also, don’t power your oxygen equipment with extension cords. In addition to avoiding electric razors and electric toothbrushes, keep the following items 6 feet away from your oxygen:
- Toys with electric motors
- Electric baseboard heaters
- Electric space heaters
- Electric Blankets
- Electric fireplaces
4. Don’t Smoke and Avoid People Who Are Smoking
As mentioned earlier, oxygen makes things burn faster and hotter. Oxygen saturates an environment, including bedding, clothing and hair. So, a small flame, heat source or spark has the potential to ignite oxygen equipment.
When you use oxygen therapy, the tubing that delivers your oxygen to you goes from your tank to your nose. To bring a lit lighter or flame anywhere near your oxygen equipment and body is extremely dangerous.
Nobody should smoke in a room, car or anywhere near where you are using oxygen. In addition, the person using oxygen therapy at home should not smoke either.
Post no smoking signs all around your home and in any room where oxygen therapy is used. Ask friends or family who continue to smoke to only smoke outside and far away from your home.
5. Keep Your Oxygen Tank Secure
Many types of oxygen equipment are bulky and heavy. This makes them prone to tipping over. Even the smaller portable oxygen concentrators can become cumbersome.
For the longevity of your oxygen tanks and cylinders, make sure to store them in well-ventilated places where they can be properly secured.
For people who use compressed oxygen tanks, the contents inside the tanks are under pressure. Should the valve at the top become damaged or begin to leak, the oxygen could spray out of the tank very rapidly and turn the tank into a projectile missile.
For safety, compressed oxygen cylinders must be placed in a secure position or attached to a carrier.
Moving Forward with Oxygen Therapy at Home
Following these safety tips for oxygen therapy at home will help you stay safe and ensure you receive your prescribed amount of oxygen. Always use your oxygen therapy at home exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
In addition, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for your specific type of oxygen therapy. If you’re unsure or have questions about using your oxygen therapy at home, talk with your doctor or oxygen supplier.

Christine Kingsley, APRN is the Health and Wellness Director at the Lung Institute where she focuses on providing helpful online resources for people looking for information on various lung diseases, breathing exercises, and healthy lifestyle choices. She advocates for holistic care that involves working with your doctor to explore all options including traditional and alternative care while focusing on diet and exercise as proactive measures.